AMD Ryzen 5 1600 Review
Written by Antony Leather
May 11, 2017 | 10:49
Tags: #1600 #1600x #1700 #am4 #amd-ryzen-5-1500x-review #amd-ryzen-5-1600-review #amd-ryzen-7-1700x-review #amd-ryzen-7-1800x-and-am4-platform-review #best-gaming-cpu #overclocking #ryzen #ryzen-1600x #ryzen-1700x #ryzen-5 #x370-1800x
Companies: #amd

Power Consumption
For all of the overclocked performance tests, we disable all power-saving technology in order to give us a consistent set of results, and also best-case performance numbers - even though technologies such as Intel's SpeedStep might only take microseconds to kick in, that can make a difference in some tests.However, for the stock speed results and power consumption tests, we re-enable everything in order to get a real-world power draw. The power draw is measured via a power meter at the wall, so the numbers below are of total system power draw from the mains, not the power consumption of a CPU itself. Measuring the power draw of any individual component in a PC is tricky to impossible to achieve.
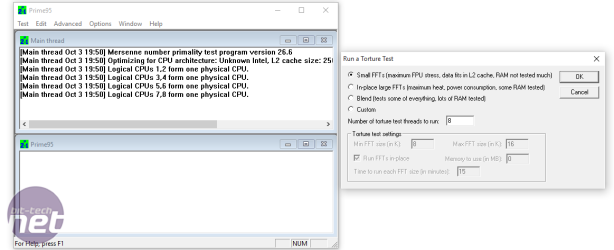
We use Prime95's small FFTs test to put the CPU under 100 percent load, while idle power results are taken with the PC sitting at a Windows Aero-enabled desktop.
Power Consumption (Idle)
Windows 10 desktop
- Intel Core i3-7350K
- Intel Core i7-7700K
- Intel Core i5-7600K
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600X (3.95GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 7 1700
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600
- AMD Ryzen 5 1500X
- Intel Core i7-7700K (5GHz)
- Intel Core i3-7350K (5GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 7 1700 (4.05GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 5 1500X (4GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600 (3.9GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600X
- Intel Core i5-7600K (5.1GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6850K
- Intel Core i7-6850K (4.2GHz)
-
-
47
-
-
-
50
-
-
-
50
-
-
-
57
-
-
-
57
-
-
-
59
-
-
-
59
-
-
-
64
-
-
-
65
-
-
-
66
-
-
-
71
-
-
-
73
-
-
-
73
-
-
-
73
-
-
-
91
-
-
-
121
-
0
25
50
75
100
125
Watts (lower is better)
-
Power Consumption
Power Consumption (Load)
Prime95 small FFTs test
- Intel Core i3-7350K
- Intel Core i5-7600K
- AMD Ryzen 5 1500X
- Intel Core i3-7350K (5GHz)
- Intel Core i7-7700K
- AMD Ryzen 7 1700
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600
- AMD Ryzen 5 1500X (4GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600X
- Intel Core i7-6850K
- Intel Core i7-7700K (5GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6900K
- Intel Core i5-7600K (5.1GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600 (3.9GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 5 1600X (3.95GHz)
- Intel Core i7-6850K (4.2GHz)
- AMD Ryzen 7 1700 (4.05GHz)
-
-
89
-
-
-
113
-
-
-
122
-
-
-
125
-
-
-
129
-
-
-
132
-
-
-
146
-
-
-
154
-
-
-
158
-
-
-
178
-
-
-
184
-
-
-
187
-
-
-
188
-
-
-
200
-
-
-
203
-
-
-
220
-
-
-
236
-
0
50
100
150
200
250
Watts (lower is better)
-
Power Consumption









Want to comment? Please log in.